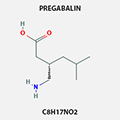
 PREGABALIN
PREGABALIN
|
148553-50-8 |
Pregabalin is indicated for management of neuropathic pain associated with diabetic peripheral neuropathy.
|
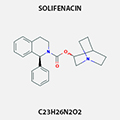 SOLIFENACIN
SOLIFENACIN
|
242478-37-1 |
Solifenacin is an anticholinergic and antispasmodic agent used to treat urinary
incontinence and the overactive bladder syndrome.
|
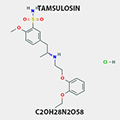 TAMSULOSIN
TAMSULOSIN
|
106133-20-4 |
Treatment of the signs and symptoms of benign prostatic hyperplasia (BPH).
|
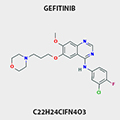 GEFITINIB
GEFITINIB
|
184475-35-2 |
Treatment of locally advanced or metastatic non-small cell lung cancer
|
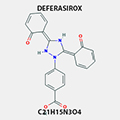 DEFERASIROX
DEFERASIROX
|
201530-41-8 |
Management of chronic Iron overload due to blood transfusion or non-transfusion
dependent THALASSEMIA.
|
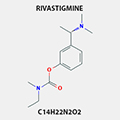 RIVASTIGMINE
RIVASTIGMINE
|
129101-54-8 |
Central nervous system and is used for the treatment of Dementia in Alzheimer disease and Parkinson disease.
|
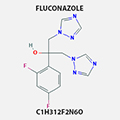 FLUCONAZOLE
FLUCONAZOLE
|
86386-73-4 |
Oropharyngeal candidiasis and cryptococcal meningitis in AIDS
|
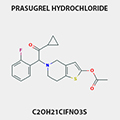 PRASUGREL HYDROCHLORIDE
PRASUGREL HYDROCHLORIDE
|
389574-19-0 |
Prevent Thrombosis in patients with acute coronary syndrome unstable angina and myocardial infraction ,
|
 ESOMEPRAZOLE MAGNESIUM
ESOMEPRAZOLE MAGNESIUM
|
217087-09-7 |
Esomeprazole
is used to treat certain stomach and problems: (such as acid reflux, ulcers). It works by decreasing the amount of acid your
stomach makes. It relieves symptoms such as heartburn, difficulty swallowing, and persistent cough. This medication helps
heal acid damage to the stomach and oesophagus, helps prevent ulcers, and may help prevent cancer of the oesophagus.
Esomeprazole belongs to a class of drugs known as proton pump inhibitors (PPIs).
|
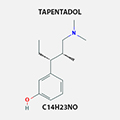 TAPENTADOL
TAPENTADOL
|
175591-09-0 |
Treatment of moderate to severe pain, and of pain associated with Diabetic Neuropathies
|
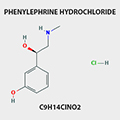 PHENYLEPHRINE HYDROCHLORIDE
PHENYLEPHRINE HYDROCHLORIDE
|
61-76-7 |
Phenylephrine is used for the temporary relief of stuffy nose, sinus, and ear
symptoms caused by the common cold, flu, allergies, or other breathing illnesses
(e.g., sinusitis, bronchitis).
|
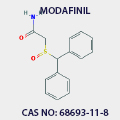 MODAFINIL
MODAFINIL
|
CAS NO: 68693-11-8 |
Modafinil and its R-enantiomer armodafinil are central nervous system stimulants
used to improve wakefulness in patients with excessive sleepiness. Both modafinil
and Armodafinil are associated with a low rate of serum aminotransferase
elevations during therapy, but they have not been implicated in cases of
clinically apparent acute liver injury.
|
 PREGABALIN
PREGABALIN
 SOLIFENACIN
SOLIFENACIN
 TAMSULOSIN
TAMSULOSIN
 GEFITINIB
GEFITINIB
 DEFERASIROX
DEFERASIROX
 RIVASTIGMINE
RIVASTIGMINE
 FLUCONAZOLE
FLUCONAZOLE
 PRASUGREL HYDROCHLORIDE
PRASUGREL HYDROCHLORIDE
 ESOMEPRAZOLE MAGNESIUM
ESOMEPRAZOLE MAGNESIUM
 TAPENTADOL
TAPENTADOL
 PHENYLEPHRINE HYDROCHLORIDE
PHENYLEPHRINE HYDROCHLORIDE
 MODAFINIL
MODAFINIL
